Solenoid vs. Solenoid Valve: Understanding the Basics
When it comes to controlling the flow of liquids or gases, you’ve probably come across terms like “solenoid” or “solenoid valve.” But what exactly do these terms mean, and why are they important? Whether you’re an engineer, a DIY enthusiast, or just curious, this blog will break things down for you in simple, easy-to-understand language.
We’ll cover what solenoids and solenoid valves are, how they work, and their applications in everyday life. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the topic—and maybe even some fun facts to share.
Contents
What Is a Solenoid?
Let’s start with the basics: a solenoid is essentially a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when electricity passes through it. Think of it as the “muscle” in electrical systems—it converts electrical energy into mechanical motion.
Key Features of a Solenoid:
- Electromagnetic Functionality: It relies on electricity to create a magnetic field.
- Versatile: Used in various applications, from cars to doorbells.
- Compact Design: Small but powerful, solenoids fit into tight spaces.
How Does It Work?
When an electric current flows through the solenoid, it creates a magnetic field. This field can move a metal core (also known as a plunger) inside the coil. This movement is what powers devices or systems connected to the solenoid.
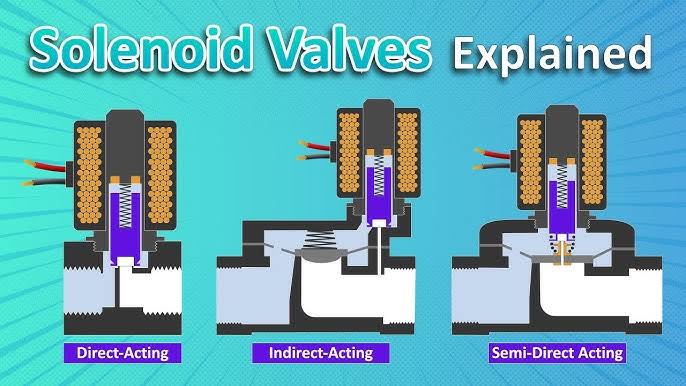
What Is a Solenoid Valve?
Now let’s add another layer: a solenoid valve. A solenoid valve is a device that uses a solenoid to control the flow of liquids or gases. Essentially, it’s the “brain” that decides when to open or close a pathway, based on electrical signals.
Key Features of a Solenoid Valve:
- Precision Control: Allows or blocks the flow of fluids or gases.
- Automated Operation: Works with electrical signals, so there’s no need for manual adjustments.
- Wide Application Range: Used in industries like agriculture, automotive, and healthcare.
How Does It Work?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- When the solenoid coil is energized (electricity flows through it), the magnetic field moves the plunger.
- This movement either opens or closes the valve, controlling the flow of the liquid or gas.
- When the electricity stops, the plunger returns to its original position, reversing the valve’s state.
Solenoid vs. Solenoid Valve: What’s the Difference?
Although they’re closely related, solenoids and solenoid valves serve different purposes:
| Feature | Solenoid | Solenoid Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts electrical energy to motion | Controls the flow of fluids or gases |
| Components | Wire coil and plunger | Solenoid plus valve mechanism |
| Applications | Door locks, electric bells | Irrigation systems, fuel controls |
Common Applications of Solenoid Valves
You might be surprised at how often solenoid valves appear in everyday life. Here are a few examples:
- Home Appliances
- Washing machines and dishwashers use solenoid valves to control water flow.
- Automotive Systems
- Fuel injectors rely on solenoid valves to regulate fuel delivery to the engine.
- Medical Equipment
- Devices like ventilators use solenoid valves for precise airflow control.
- Irrigation Systems
- In agriculture, solenoid valves automate water flow, saving time and effort.
- Industrial Processes
- Factories use solenoid valves to control the flow of chemicals or other fluids in production lines.
Why Are Solenoid Valves Important?
Solenoid valves play a critical role in automation and efficiency. Imagine having to manually control water flow every time you do laundry or water your garden. Solenoid valves make these processes seamless, saving time and ensuring precision.
Choosing the Right Solenoid Valve
If you’re shopping for a solenoid valve, here are some factors to consider:
- Material: Choose a valve material that suits the liquid or gas it’ll handle.
- Voltage: Ensure compatibility with your system’s electrical setup.
- Pressure Requirements: Select a valve that can handle the required pressure levels.
- Size: Pick a valve that fits your system’s dimensions.
Conclusion
Whether it’s opening your car door or regulating water in your washing machine, solenoids and solenoid valves are everywhere. Understanding their function and differences can help you make informed decisions, especially if you’re working on a project or troubleshooting an issue.
Next time you hear a buzz or click in your home appliances or car, remember: there’s probably a solenoid or solenoid valve at work, making life easier and more efficient.
FAQs About Valves
Q1: What is the main purpose of a solenoiid?
A solenoid converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, powering various devices.
Q2: How is a solenoid valve different from a solenoid?
A solenoid is the component that creates motion, while a solenoid valve uses that motion to control fluid or gas flow.
Q3: Where are solenoid valves commonly used?
You’ll find them in home appliances, automotive systems, medical devices, irrigation setups, and industrial processes.
Q4: Can I repair a solenoid valve if it stops working?
Yes, but it depends on the issue. Common fixes include cleaning the valve or replacing the solenoid coil.
Q5: Are these valves energy-efficient?
Yes, they only use electricity when switching states, making them energy-efficient for automated systems.
By understanding these components, you can better appreciate the engineering marvels that quietly run our modern world!


A person necessarily assist to make seriously posts I would
state. That is the very first time I frequented your website page and thus far?
I surprised with the analysis you made to make this actual publish extraordinary.
Wonderful task!
Visit my blog … nordvpn coupons inspiresensation (tinyurl.com)
This paragraph is in fact a good one it assists new the web visitors, who
are wishing in favor of blogging.
my web blog; nordvpn coupons inspiresensation (http://cfg.me/nordvpn-coupons-inspiresensation–98798)
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful article. Many
thanks for providing this info.
Feel free to visit my web-site Eharmony Special Coupon Code 2025
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check
out your website on my iphone during lunch break. I love the
information you present here and can’t wait to take a look
when I get home. I’m surprised at how quick your blog loaded on my cell phone
.. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, wonderful site!
My website vpn
Hi, yup this article is really pleasant and
I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging.
thanks. gamefly https://tinyurl.com/2ah5u2sb
These are in fact enormous ideas in about blogging.
You have touched some fastidious factors here. Any way keep up wrinting.
What is vpn stand for https://tinyurl.com/24dyn2m6
I visited multiple blogs however the audio quality for audio
songs existing at this website is actually wonderful.